Author: Associate Vice President, Analytics and Data Strategy, Quantzig.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Risk Management in Banking
The concept of risk management is not new; it has long been a fundamental responsibility of the C-suite. What has changed is the heightened awareness of its importance. The banking sector plays a pivotal role in fostering economic growth, but its inherent vulnerabilities make it susceptible to various risks that can have far-reaching impacts. Consequently, robust risk management strategies are crucial for mitigating these risks and ensuring the stability of the banking industry. This is where risk management in banking assumes paramount importance, as it enables financial institutions to proactively address potential threats and maintain a secure financial environment.
For organizations still using traditional risk management approaches, meeting these expectations is a significant challenge. It is no surprise, then, that many are turning to risk analytics. An expert domain for Quantzig Analytical platform. Let us delve into the significance of risk management in banking and its role in mitigating risks within the industry.
Book a demo to experience the meaningful insights we derive from data through our analytical tools and platform capabilities. Schedule a demo today!
Request a Free DemoWhat does Risk Management in Banking mean?
Risk management in banking is paramount, given the sector’s pivotal role in financial stability. Banks must systematically identify, assess, and mitigate risks associated with their operations and investments. This involves deploying a robust framework encompassing risk assessment, mitigation, monitoring, and reporting. By proactively addressing risks, banks safeguard their operations, stakeholders, and clients. In today’s complex regulatory and economic landscape, effective risk management is essential. Tools like risk monitoring dashboards and insurance provide additional support. Embracing innovation while managing risks ensures that banks stay resilient and adaptive, aligning risk considerations with strategic goals for sustainable growth.
Experience the advantages firsthand by testing a customized complimentary pilot designed to address your specific requirements. Pilot studies are non-committal in nature.
Request a free trial nowThe Importance of Risk Management in Banking
The banking industry is by far one of the largest industries in the world. In the US, insurance, real estate, and financial industry account for 20% of the total GDP. In order to keep the economy smoothly flowing, it is essential that the banking industry operates seamlessly. However, the truth is that the banking sector is far from stable, as banks face numerous risks that threaten not only their profits but also the economic balance as a whole. As a result, it is essential that banks perform proper risk analysis and mitigate such perils for smooth operations. Keeping risks unchecked can lead the world towards financial meltdown as witnessed in the 2008 global crisis. So what are the kind of risks faced by the banks that need to be regularly monitored?
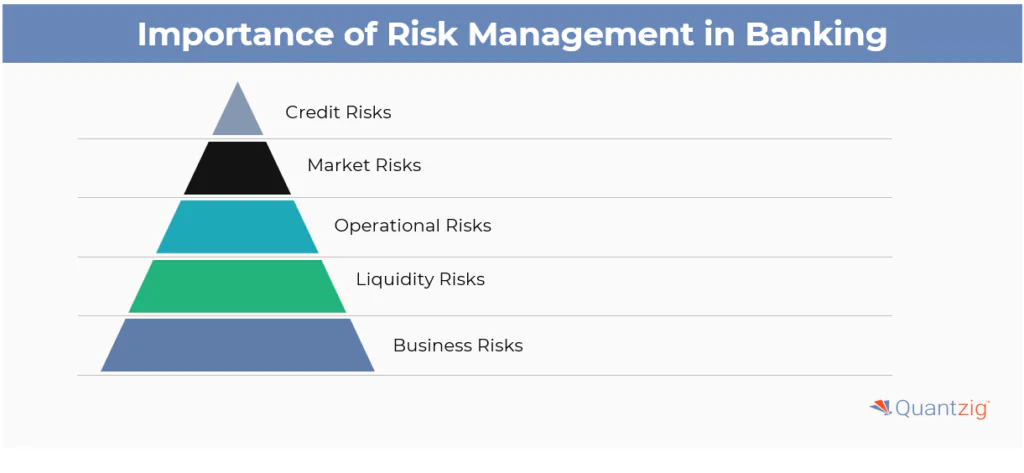
Credit Risks
Credit risk can be defined as a risk that a borrower or the counterparty will fail to meet their obligations by agreed terms. Such risks occur due to borrowers’ inability to pay back loans arising out of interbank transactions, trade financing, foreign exchange transactions, swaps, bonds, financial futures, options, guarantees, and the settlement of transactions. To simplify the matter, a $100 borrowed and not paid back will result in banks taking the loss in full. Additionally, banks will have to redress the money from their lenders who can be the government, other banks, or the general public. Such losses in large amounts can cause a serious dent in the economy. The banking industry usually declares a high rate of interest for borrowers who are associated with high credit risk. Banks need to perform timely risk analysis at an individual level to protect its wealth.
Market Risks
“Mutual fund investments are subject to market risks.” You may have heard this statement a thousand times over in the banking industry. So what is market risk? It is the risk that causes losses in the bank’s trading books due to changes in interest rates, credit spreads, equity prices, foreign exchange rates, commodity prices, and other indicators. However, this type of risk only troubles players who are into the investment banking space since they are active in the capital markets. Market risks are hard to assess as some factors are highly volatile like commodity prices, whereas some are stable, but small deviations can cause big consequences like interest rates. Proper risk analysis can be carried out by dividing it as per their potential cause, i.e., interest rate risk, equity risk, currency risk, and commodity risk.
Operational Risks
Losses that could arise from failed or inadequate internal processes, people, and systems or from external events is termed as operational risk. It also includes legal risk but does not incorporate strategic or reputation risk. Humans are prone to making errors and mistakes, and such errors can occur in the banking industry due to improper operational risk analysis. Filling incorrect information while clearing a financial instrument can cause loss of time to rectify that error and in some cases loss of money due to improper crediting of balance. Apart from human risk, operational risk can also occur due to system risk or process risk.
Liquidity Risks
Liquidity risk arises when banks perform inadequate risk analysis relating to the marketability of an investment that cannot be sold quickly enough to prevent a loss. In simple terms, it is a risk that disables a bank from carrying out its day-to-day cash transactions. Even though it may seem like a theoretical example, it happened in Northern England when one of the banks was taken over by the government due to its inability to repay the investors during the 2008 global crisis.
Business Risk
Businesses in the banking industry may be unable to meet its anticipated profit targets due to various reasons. Sometimes they may even incur a loss in place of making a profit. In the case of banks and the financial institutions, missing the target can have severe implications as banks will have to shuffle their investment and public money. Business risk arises due to the failure of the bank’s long-term strategy and errors in the estimation and forecasting of profit metrics. A proper business risk management strategy can ensure sustainability even in the harshest economic environment. Conducting thorough risk analysis by guaranteeing flexibility and adaptability to the market condition can help banks avoid business risk.
Which Businesses Use Risk Management Data Analytics?
For any organization, finding the right balance between risk and innovation is crucial. Every organization and industry must employ techniques to remain competitive, compliant, and functional.
Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance
In the financial sector, particularly during forecast periods, risk analytics play a vital role. The banking sector relies extensively on system integration, modeling, and the quality and sourcing of data. Given the highly regulated nature of banking and the significant penalties for non-compliance, effective risk management is essential.
Telecommunications
In each forecasting period, the telecommunications sector is expected to invest increasingly in risk analytics. The stiff competition in this industry has led to reduced revenues, and the sector faces significant fraud-related losses. To address these challenges, many telecom operators are adopting risk analytics solutions to prevent revenue leakage and boost earnings.
Government Services
The government services sector utilizes risk analytics solutions extensively for risk prediction and prevention, as well as for activities like weather forecasting, border security management, policy control, and strategic decision-making. High-profile attacks on governments in recent years have exposed system vulnerabilities and the severe consequences of data hacks.
Healthcare Sector
In the healthcare industry, risk analytics are essential for ensuring patient safety and reducing the risk of drug contamination. These tools also help manage, store, and access user data securely.
Other Sectors Investing in risk management data analytics:
- Consumer Goods
- Retail
- Manufacturing
- Transportation and Logistics
- Information Technology
- Media Outlets
- Energy and Utilities
As the expansion of businesses continues, more sectors are recognizing the need to invest in risk analytics for the upcoming financial years.
Get started with your complimentary trial today and delve into our platform without any obligations. Explore our wide range of customized, consumption-driven analytical solutions services built across the analytical maturity levels.
Start your free trial nowThe Role of Risk Analytics in Modern Enterprises
The integration of big data and enhanced computing capabilities allows for more accurate risk prediction and provides actionable insights for developing effective risk strategies. Organizations can use advanced analytics to understand key risk indicators and their relative importance, enabling them to identify future risks well in advance.
For a driven enterprise in sectors like financial services, risk analytics facilitate risk aggregation, risk tracking, and risk assessment, transforming instinctive responses into data-driven decisions. Tools such as risk monitoring dashboards and spot testing ensure continuous oversight, while risk insurance offers protection against unavoidable threats.
By embracing risk and innovation, companies can balance risk pursuit with risk reduction, ensuring that risk management is deeply embedded in their operational framework and strategic initiatives. This unified approach helps businesses navigate the complex regulatory and economic environments and mitigate risks associated with lax processes and data hacks.
Challenges in the Banking Industry:
The banking industry grapples with several challenges that heighten the complexity of risk management:
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to a myriad of banking regulations poses challenges for banks. Navigating complex regulatory landscapes demands robust compliance departments and processes to avoid legal and reputational risks.
- Technological Advancements: While technology brings efficiency, it also introduces cybersecurity risks and the need for constant technological upgrades. Balancing innovation with security is a perpetual challenge for banks.
- Global Economic Dynamics: The interconnectedness of global economies means that events in one part of the world can impact banks globally. Geopolitical tensions, economic downturns, or health crises can trigger unforeseen risks.
The Risk Management Process: How It Works in Banking?
Controlling risks in the banking industry is crucial for maintaining financial stability and safeguarding the interests of customers and shareholders. Here are four key strategies for risk control:

The risk management process in banking is a multifaceted approach that involves six critical components to ensure the effective mitigation of potential threats. These components are:
- Identification: This involves defining the nature of risks, including their origin and the potential threats they pose to the bank. This step is crucial in understanding the scope of risks and prioritizing them accordingly.
- Assessment and Analysis: This component involves evaluating the likelihood and potential impact of each identified risk. This helps banks prioritize which risks require the most attention and resources.
- Mitigation: In this step, banks design and implement policies and processes to limit the likelihood of risks becoming threats and to minimize the damage that threats may cause.
- Monitoring: Continuous monitoring involves gathering data on the effectiveness of risk management strategies and incident response. This helps banks refine their approaches and stay ahead of emerging risk trends.
- Cooperation: Establishing relationships between risks and mitigation strategies across different areas of the bank’s operations enables a more centralized and coordinated threat response system.
- Reporting: Documenting and reviewing information related to banking risk management efforts helps banks gauge their effectiveness and track changes in their overall risk profile over time.
To achieve optimal risk management, these components must be executed in tandem and repeated regularly. This ensures that banks maintain a robust defense against potential risks and can adapt to evolving threats in a timely manner.
Best Practices in Risk Management
Effective risk management in banking is crucial for financial institutions to thrive in a dynamic and competitive environment. By embracing risk while developing robust mechanisms to prevent or manage them, banks can minimize losses, enhance stability, and grow responsibly.
To implement a comprehensive banking risk management plan, financial institutions should follow these key steps:
- Risk Identification and Assessment: Identify potential risks associated with operations and assess their severity and impact to prioritize mitigation efforts.
- Risk Mitigation: Implement strategies to mitigate the effects of identified risks, including risk avoidance, reduction, acceptance, and transfer.
- Risk Monitoring and Reporting: Continuously monitor operations to identify evolving risks and develop mitigation strategies. Generate regular reports to track the effectiveness of the risk management program and provide a dynamic view of the bank’s risk profile.
However, implementing a risk management strategy can be challenging due to various factors such as new regulatory rules, cybersecurity and fraud threats, increased competition, and inefficient resources and processes. An effective risk management plan serves as a roadmap for improving performance, enabling banks to allocate resources more efficiently and focus on high-priority areas.
Conclusion
In summary, banking risk management in the industry involves a combination of proactive risk assessment, diversification, regulatory compliance, and maintaining adequate capital reserves. By implementing these strategies, banks can minimize potential risks and enhance their overall stability. The banking industry’s stability hinges on proactive risk management strategies that encompass risk assessment, diversification, regulatory compliance, and capital adequacy. By implementing robust risk control measures, banks can navigate the intricate landscape of risks, ensuring ongoing stability and resilience in a dynamic financial environment.