Table of Contents
Introduction to Analytics in Telecom Sector
Fierce competition, diminishing profit margins, and high churn rates are some of the factors influencing the profit margins of telecom companies. Surviving in such a challenging market isn’t a walk in the park. It takes intensive planning and constant innovation in customer analytics in telecom to keep the customers happy and the profits flowing in the telecom industry. Although customer service and profitability can be considered as the two extreme sides of the equation, how can telecom companies achieve perfection in both areas? In a bid to remain competitive and highly efficient, telecom companies rely on some critical metrics to measure their performance and plan for the future of telecom performance analytics.
Here are some of the most important metrics used in the telecom industry to monitor performance and compare them against industry benchmarks.
Book a demo to experience the meaningful insights we derive from data through our analytical tools and platform capabilities. Schedule a demo today!
Request a Free DemoWhat is Big Data Analytics and Why Does it Matter?
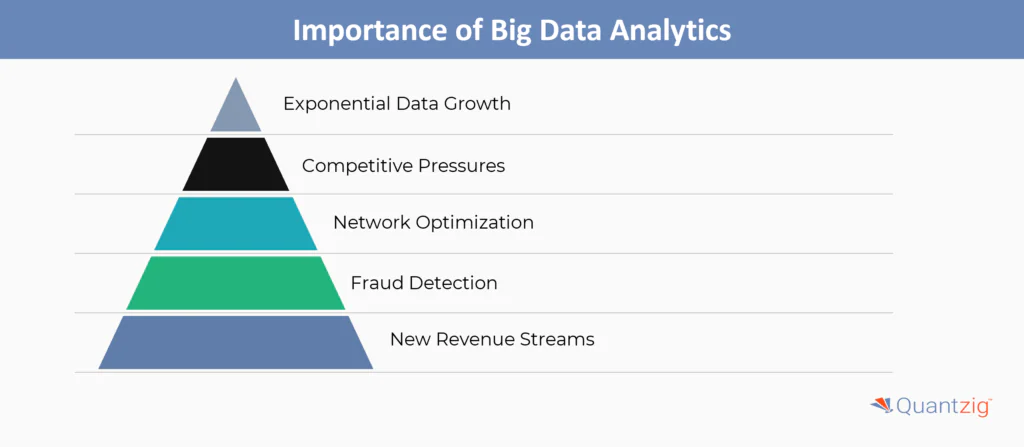
Big data analytics refers to the process of examining large and complex datasets to uncover hidden patterns, correlations, and insights that can inform business decisions. In the telecom industry, big data analytics is becoming increasingly important for several key reasons:
- Exponential Data Growth: The rise of smartphones, connected devices, and digital services has led to an explosion of data within the telecom sector. Operators are now collecting vast amounts of information from network logs, customer interactions, billing records, and more.
- Competitive Pressures: Telecom companies face intense competition, churn, and the need to differentiate their offerings. Big data analytics enables them to better understand customer behavior, preferences, and pain points to improve the customer experience.
- Network Optimization: Analyzing network performance data can help telecom providers optimize infrastructure, reduce costs, and ensure quality of service for customers.
- Fraud Detection: Big data tools can rapidly sift through large datasets to identify patterns indicative of fraudulent activities, allowing telecom companies to mitigate revenue leakage.
- New Revenue Streams: Deriving insights from customer data can uncover opportunities for new product development, targeted marketing, and personalized offerings that drive additional revenue.
In essence, big data analytics empowers telecom companies to make more informed, data-driven decisions across their operations – from network planning to customer engagement. This can lead to significant improvements in efficiency, profitability, and competitiveness within the industry.
What are the Challenges of Big Data Analytics in Telecom?
While the benefits of big data analytics are clear, telecom companies often face several challenges in effectively leveraging this technology:
- Data Silos and Integration: Telecom data resides in multiple, disparate systems, making it difficult to consolidate and analyze holistically.
- Data Quality and Governance: Telecom data can suffer from quality issues like missing values, inconsistencies, and inaccuracies, requiring robust data management practices.
- Talent and Expertise: Implementing big data analytics requires specialized skills in areas like data engineering, machine learning, and business intelligence – which can be scarce.
- Legacy Infrastructure: Many telecom providers operate on aging IT systems that may not be compatible with modern big data technologies and tools.
- Organizational Adoption: Driving cultural change and getting business stakeholders to rely on data-driven insights can be a significant hurdle.
Overcoming these challenges requires a strategic, multi-faceted approach that addresses people, processes, and technology within the telecom organization.
Ways to Overcome Telecom Data Analytics Challenges
- Overcoming telecom big data analytics challenges requires the telecom industry to adopt advanced tools and technologies and analysis techniques to handle vast amounts of data processing.
- Implementing advanced analytics platforms that incorporate AI (Artificial Intelligence) and ML (Machine Learning) can enhance real-time data processing capabilities, improving network performance and operational efficiency.
- Embracing the latest trends in data analytics and focusing on robust telecom analytics solutions will enable telecom providers to navigate the complexities of the global big data analytics market.
- Additionally, fostering a data-driven world culture within organizations and investing in skilled professionals can ensure sustainable growth and competitive advantage in the telecom analytics market.
Use Cases of Data Analytics in Telecom Sector
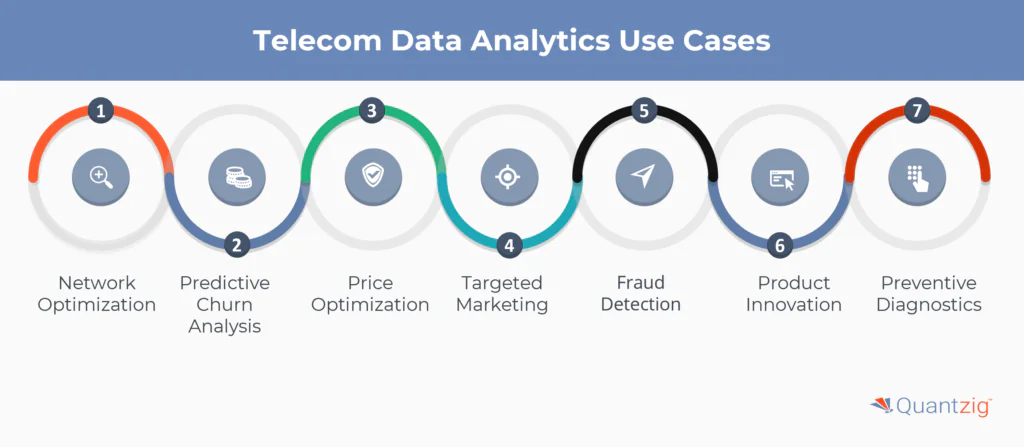
Telecom business intelligence companies are increasingly leveraging big data analytics to enhance their operations and services. By applying data-driven insights across various areas, they are able to optimize performance, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. Below is a summary of the key use cases where telecom companies are implementing big data analytics:
| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
| Network Optimization | Analyzing network performance data to identify congestion, optimize capacity, and improve service quality. |
| Predictive Churn Analysis | Using customer data to predict which subscribers are at risk of churning and proactively intervening with retention offers. |
| Price Optimization | Dynamically adjusting pricing based on factors like demand, competition, and customer willingness to pay. |
| Targeted Marketing | Leveraging customer insights to deliver personalized offers, content, and recommendations that increase engagement and loyalty. |
| Fraud Detection | Detecting anomalies and suspicious patterns in call records, usage data, and payment information to mitigate revenue leakage. |
| Product Innovation | Analyzing customer feedback and market trends to inform the development of new products and services. |
| Preventive Diagnostics | Using sensor data and predictive analytics to anticipate equipment failures and schedule proactive maintenance. |
What are the Top 4 Telecom Analytics Metrics?
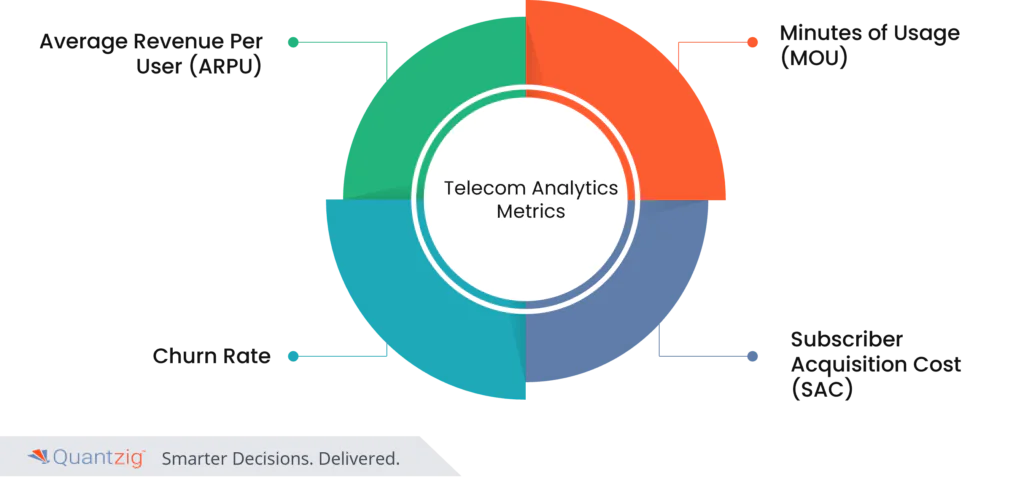
1. Average Revenue Per User (ARPU)
ARPU = Total Revenue/Number of subscribers
- As simple as it gets, it is a measure of how much revenue telecom companies generate from each user. It’s a measure to illustrate the company’s operational performance. This metric is important for telecom companies because they incur a large number of fixed costs, and they need to ascertain whether they are generating revenue that justifies their spending.
- It also paints a picture for the investors on marginal profits and costs of the company, revealing how they are utilizing the resources. It also acts as a yardstick to measure the revenue generated from high spending customers and customers who are not profitable.
- Telecom service providers have started offering bundled services in order to increase ARPU metrics. ARPU can be further broken down into revenues from voice and data or prepaid and postpaid. Some companies even consider average revenue per minute (ARPM) as metrics to measure per unit cost versus revenue.
2. Minutes of Usage (MOU)
MOU = Total Usage Time in minutes per month/Number of customers
- Minutes of Usage (MOU) is the total time in minutes, used by a customer on their mobile phone, within a particular time frame. MOU can be further segmented into postpaid and prepaid MOU or incoming and outgoing MOU.
- Since most telecom companies offer package voice services to their customer, it is essential to know the MOU for each customer. Also, knowing the average MOU for a cohort can help telecom companies to design a promotional campaign that can be profitably catered to a group of people. Additionally, it also helps telecom companies ascertain rates for bundled voice packs.
3. Churn Rate
Churn Rate = (Customers end of the month – Customers beginning of the month)/Customers beginning of month x 100 (expressed in percentage)
- Churn rate is the metric that measures how many subscribers leave the service provider in favor of competitors. Companies are trying hard to reduce their churn rates, by implementing customer lifetime value (CLV) calculations to customize offerings for each customer.
- The advent of data analytics has enabled them to build predictive models, which helps them in identifying customers who may churn in the near future so that corrective measures can be taken in time.
4. Subscriber Acquisition Cost (SAC)
SAC = Total Spend/Additional Subscribers
- Subscriber acquisition cost is a measure used within the telecom industry to figure out the total average cost of adding a new subscriber to the list.
- These metrics take into consideration all marketing costs including dealers’ commission, sales cost, marketing, and advertising cost, terminal subsidy, and distribution cost that are spent to acquire a new customer.
- This metric can later be compared to ARPU to figure out if it’s worth spending so much on the acquisition or if they can afford to increase the spending to expand the customer base.
Experience the advantages firsthand by testing a customized complimentary pilot designed to address your specific requirements. Pilot studies are non-committal in nature.
Request a Free PilotUpcoming Trends in Data Analytics in Telecom Sector
As the telecom sector continues to evolve, several key trends are shaping the future of data analytics in this industry:
- Edge Computing: Performing data processing and analysis closer to the network edge to reduce latency and enable real-time decision-making.
- Data-as-a-Service (DaaS): Providing on-demand access to telecom data through cloud-based platforms, reducing the need for local data management.
- Advanced AI and Machine Learning: Leveraging sophisticated algorithms to uncover deeper insights, automate decision-making, and enable predictive capabilities.
- Hybrid Cloud Architectures: Combining private and public cloud infrastructure to gain the benefits of both flexibility and security.
- 5G Network Analytics: Optimizing the performance and utilization of 5G networks through advanced analytics capabilities.
These trends highlight the telecom industry’s ongoing transformation, where data and analytics are becoming increasingly central to driving innovation, efficiency, and customer-centricity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the four key metrics in the telecom industry serve as indispensable tools for making informed and strategic decisions. From customer satisfaction and churn rates to network performance and revenue per user, these metrics provide a holistic view of the industry landscape. By leveraging these insights, telecom companies can enhance customer experiences, optimize network efficiency, and drive sustainable revenue growth. The dynamic nature of the telecommunications analytics solutions sector demands continuous monitoring and adaptation to evolving trends. Embracing these metrics not only empowers decision-makers with real-time data but also enables them to proactively address challenges and capitalize on opportunities. As technology advances and consumer expectations evolve, a proactive approach guided by these metrics is essential for staying competitive and ensuring long-term success in the ever-evolving telecom landscape.
Get started with your complimentary trial today and delve into our platform without any obligations. Explore our wide range of customized, consumption driven analytical solutions services built across the analytical maturity levels.
Start your Free Trial