Author: Vice President, Data Analytics, Quantzig.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Robotic Surgeries Pros and Cons
The healthcare industry is gradually transforming itself into an epitome of advanced technology and the wonders it can work. From using superior medical devices for treatment to ensuring better patient care and facilities, healthcare companies are breaking new grounds with each passing year. One such intriguing innovation in healthcare is the incorporation of robotic surgery. Robotic surgery is a type of minimally invasive surgery that operates on patients through miniaturized surgical instruments. Though this technology was met with skepticism in the initial days of inception, medical professionals have slowly started contemplating over the brighter side of robotic surgery. But the big question here is ‘is the use of robotics in surgery all set to replace surgeons?’
Book a demo to experience the meaningful insights we derive from data through our analytical tools and platform capabilities. Schedule a demo today!
Request a Free DemoWhat is Robotic Surgery?

Robotic surgery refers to the use of advanced robotic systems that enable surgeons to perform complex medical procedures with greater precision, flexibility, and control than traditional open or laparoscopic surgery. These robotic systems, such as the da Vinci Surgical System, utilize miniaturized instruments and high-definition 3D cameras, allowing surgeons to operate through small incisions while maintaining a high level of dexterity and visual acuity. Robotic surgery has been increasingly adopted across various medical specialties, including urology, gynecology, and cardiothoracic surgery, as it offers patients reduced pain, shorter recovery times, and improved clinical outcomes.
Examples of Robotic Surgery
Here are some common examples of robotic surgery that highlight its versatility across various specialties:
- Prostatectomy: Removal of the prostate gland.
- Hysterectomy: Removal of the uterus.
- Cardiac procedures: Includes coronary artery bypass and mitral valve repair.
- Kidney procedures: Such as partial nephrectomy and pyeloplasty.
- Gallbladder removal: Known as cholecystectomy.
- Colorectal surgery: Including colon resection and rectal cancer removal.
- Gynecological oncology procedures: For removing cervical, uterine, and ovarian cancers.
- Thoracic surgeries: Such as lung cancer removal and esophageal procedures.
- Head and neck surgeries: Involving thyroid, parathyroid, and oral cancer removal.
- Joint replacement: Covering partial knee and total hip replacement.
- Pediatric procedures: Addressing congenital heart defects and urological conditions.
The advantages of robotic surgery include precision in surgery, reduced recovery time, less blood loss, and enhanced visualization in surgery. However, it is important to consider the disadvantages of robotic surgery, including the cost of robotic surgery and the necessity for surgeon training for robotic systems.
As robotic surgical systems continue to evolve, their use in minimally invasive surgery is becoming more common, leading to improved patient outcomes with robotic surgery. Despite these benefits, there are also robotic surgery risks and potential complications of robotic surgery that need to be acknowledged.
In comparison to traditional surgery, robotic techniques have shown improved success rates and enhanced patient safety in robotic surgery. Surgeon experience with robotic surgery plays a crucial role in achieving optimal results, especially in robotic surgery in oncology, where specialized knowledge can significantly impact patient care.
Looking ahead, the future of robotic surgery appears promising, with ongoing advancements in robotic surgery technology paving the way for even more innovative applications across diverse surgical fields..
What is Robotic Surgery Most Used For?

Robotic surgery is most commonly used for the following procedures:
- Urological surgeries: Robotic surgery is widely used for prostate removal (prostatectomy) and kidney procedures.
- Gynecological surgeries: Robotic techniques are employed for hysterectomies, myomectomies (removal of uterine fibroids), and other complex gynecological procedures.
- General surgeries: Robotic surgery is increasingly used for hernia repairs, gallbladder removals, colon resections, and other abdominal procedures.
- Thoracic surgeries: Robotic systems enable minimally invasive approaches for lung procedures, esophageal surgeries, and mediastinal mass removals.
- Cardiac surgeries: Robotic-assisted techniques are used for coronary artery bypass, mitral valve repair, and other heart procedures, leading to faster recovery and return to work for patients.
- Head and neck surgeries: Robotic surgery provides improved access and visualization for complex procedures in the head and neck region.
- Pediatric surgeries: Robotic platforms are used for a variety of pediatric procedures, including kidney, bladder, and airway surgeries.
The versatility of robotic surgery allows it to be applied across various specialties, particularly in procedures involving tight, cramped, or hard-to-reach areas where the robot’s 3D camera and wristed instruments provide significant advantages over traditional open or laparoscopic approaches.
What are the Advantages of Robotics in Surgery?
Here are the key advantages of using robotic systems in surgical procedures:
1. Minimally Invasive
- One of the major advantages of robotics in surgery is the fact that instead of operating on patients through large incisions, surgeons can now perform operations with minimal incisions, without compromising on the safety.
- Moreover, tremors in the surgeon’s hands are filtered out by the robotic arms, which eliminates the inadvertent nicks or punctures that can cause bleeding and infections.
2. Faster Recovery
- The human body is more likely to recover faster from robotic surgery primarily due to the minimally invasive methods used.
- Though the healing process varies from person to person, it has been commonly observed that patients are able to resume normal activities, including working, within several weeks after robotic surgery.
3. Minimal Blood Loss and Pain
- Greater precision and smaller incisions are one of the prime advantages of robotics in surgery as patients tend to experience lesser pain pre and post the surgery.
- Furthermore, this means that patients will be required to take fewer painkillers in the recovery stage; thus, eliminating the risk of addiction. Robotic surgery also eliminates the need for blood transfusions, which ensures that there is minimal blood loss.
4. Lower Chances of Infection
- Infections are common in surgical procedures. Infections tend to prolong the recovery process.
- In this case, since robotic surgery is minimally invasive, the risk of developing an infection is minimal, which also avoids the potential complications associated with infections.
5. Improved Precision and Dexterity
- Robotic arms have a greater range of motion and can make smaller, more precise movements compared to the human hand.
- This allows surgeons to operate in tight, confined spaces and perform complex procedures with enhanced accuracy.
6. Enhanced Visualization
- Robotic surgical systems provide high-definition, 3D visualization of the surgical site, giving the surgeon an immersive and magnified view.
- This improved visualization enables better identification of anatomical structures and pathologies.
7. Improved Ergonomics
- The surgeon controls the robotic arms from an ergonomic console, reducing physical strain and fatigue compared to traditional open or laparoscopic surgeries.
- This can lead to improved surgeon performance and reduced risk of occupational injuries.
8. Expanded Surgical Capabilities
- Robotic systems allow surgeons to perform complex procedures that may be difficult or impossible with conventional techniques.
- This includes surgeries in hard-to-reach areas of the body, such as the heart, prostate, or gynecological organs.
9. Potential for Improved Outcomes
- The enhanced precision, visualization, and minimally invasive approach of robotic surgery can contribute to better patient outcomes, such as reduced complications, faster recovery, and improved long-term results.
10. Telesurgery and Remote Access
- Robotic systems enable the possibility of telesurgery, where a surgeon can remotely control the robotic arms and perform procedures on a patient located elsewhere.
- This can improve access to specialized surgical care, especially in remote or underserved areas.
Overall, the advantages of robotic surgery lie in its ability to enhance surgical capabilities, improve patient outcomes, and provide a more ergonomic and comfortable experience for the surgical team.
Also Read: Track Business Progress with Marketing Analytics Dashboard
Experience the advantages firsthand by testing a customized complimentary pilot designed to address your specific requirements. Pilot studies are non-committal in nature.
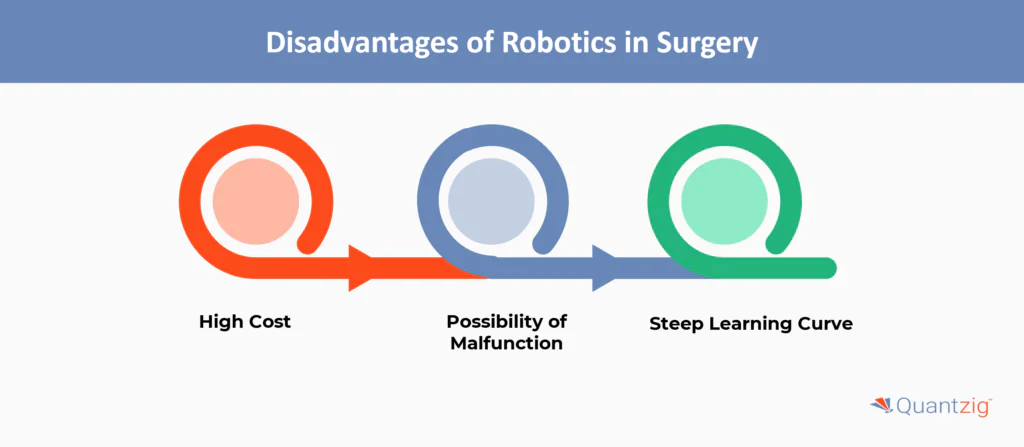
Request a Free PilotWhat are the Disadvantages of Robotics in Surgery?
1. High Cost
- Robotic surgery is more expensive when compared to the traditional surgery, making it one of the key disadvantages of robotics in surgery. The costs are found to be generally higher due to the cost involved in setting up robotic surgery devices.
- Furthermore, there is also an additional cost incurred by healthcare companies in the training of a surgeon in using robotics in surgery and the lost time that can be used to operate on patients.
2. Possibility of Malfunction
- Malfunction and repairs are regarded as one of the prime disadvantages of robotics in surgery. As surgeries are highly risky and sensitive, healthcare companies might have to pay a heavy price in case of any error or malfunction.
- However, a replacement robot can be put in place for such a mishap. Also, in such cases, the surgeon can also be trained to take over the robot and continue the operation.
3. Steep Learning Curve
- Surgeons often tend to find the learning curve in robotic surgery to be steeper. On an average, it takes at least hundreds of surgeries for a surgeon to master the use of robotics in surgery.
- This extra training time can perhaps be better used to train a surgeon’s skill in manual operation.
Also Read: Maximizing Marketing Budgets with Campaign ROI Analysis
Get started with your complimentary trial today and delve into our platform without any obligations. Explore our wide range of customized, consumption driven analytical solutions services built across the analytical maturity levels.
Start your Free Trial TodayConclusion
Robotic surgeries offer significant advancements in minimally invasive procedures through precise robotic devices and surgical instruments controlled by sophisticated controllers. They mitigate risks associated with traditional surgeries such as infection, blood loss, and extended hospital stays, promising quicker recovery time, reduced pain, and minimal scarring. However, concerns remain regarding complications and expense associated with robotic technology. Despite these challenges, the evolution of robotic arms in surgery represents a transformative shift, balancing potential benefits with ongoing refinements needed to optimize patient outcomes and healthcare efficiency.