To compete in today’s digital economy, organizations collect vast amounts of data from sources like customer interactions, internal operations, and social media. While this data holds potential for valuable insights, its value depends on how well it’s managed.
DLM is a comprehensive strategy that oversees data from its initial creation to its eventual disposal. It ensures that data is securely stored, properly maintained, and remains compliant with relevant regulations throughout its lifecycle. This structured approach supports data availability, integrity, and regulatory adherence.
Table of Contents
Goals of Data Lifecycle Management
Effective DLM ensures that data is properly governed from creation to disposal, maintaining its security, integrity, and compliance with evolving regulations. In 2025, as businesses collect ever-larger volumes of data from diverse sources, managing this data through a structured data lifecycle has become vital for deriving meaningful insights and achieving operational excellence. A well-structured DLM strategy encompasses several stages—data creation, storage, retrieval, maintenance, archiving, and disposal—allowing organizations to keep data accessible, secure, and compliant. Whether it’s enhancing data security, reducing costs, or supporting data-driven decision-making, DLM plays a pivotal role.
Companies like Quantzig provide expertise across the data management lifecycle, helping implement effective policies for governance, architecture, backup, and secure data disposal. With the right DLM tools and technologies, such as encryption, access control, and data quality management, organizations can address common challenges like data overload, silos, and compliance issues.
Unlike broader information lifecycle frameworks, DLM focuses specifically on structured and unstructured data, ensuring raw data is consistently managed across all phases. The benefits are clear: improved data availability, integrity, and business agility, along with reduced risks and storage costs. As businesses look to 2025 and beyond, mastering data lifecycle management is essential for transforming raw data into a strategic asset that powers innovation, boosts customer experience, and sustains a competitive edge.
Importance of Data Lifecycle Management
Data lifecycle management is crucial for several reasons. It is essential to know them all to choose which one requires more attention for your problems:
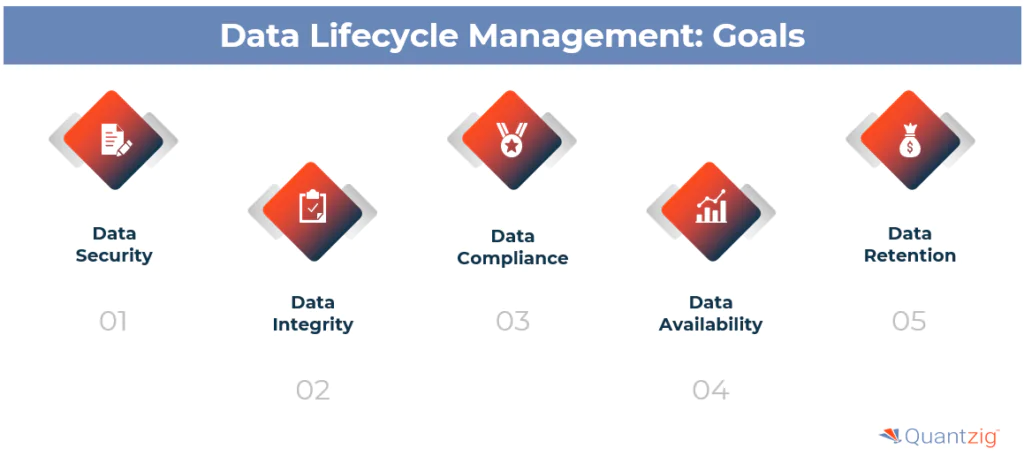
Data Security:
Proper management of data engineering ensures that it is secure and protected from unauthorized access. With the increasing frequency of data breaches and cyber attacks, it is essential to have robust security measures in place to protect sensitive data.
Data Compliance:
Compliance with regulatory requirements is ensured, reducing the risk of fines and reputational damage. Organizations are subject to various data protection laws and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), which require strict data management practices.
Data Integrity:
Data integrity is maintained, ensuring that data remains accurate and complete. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to poor decision-making and negatively impact business outcomes.
Data Availability:
Data is accessible and usable when needed, supporting business operations and decision-making. Effective data management ensures that data is readily available to those who need it, when they need it.
Cost Savings:
Effective DLM can reduce storage costs by ensuring that data is properly archived and disposed of. Storing unnecessary data can be costly, and effective DLM helps organizations optimize their storage resources.
Book a demo to experience the meaningful insights we derive from data through our analytical tools and platform capabilities. Schedule a demo today!
Request a Free Demo6 Key Stages of Data Lifecycle Management
The key stages of data lifecycle management are:

- Data Creation: Data is created and stored in a secure and organized manner. This stage involves defining data requirements, establishing data sources, and implementing data capture processes.
- Data Storage: Data is stored in a secure and accessible manner. This stage involves selecting appropriate storage solutions, implementing backup and recovery procedures, and ensuring data redundancy.
- Data Retrieval: Data is retrieved and used for business operations and decision-making. This stage involves developing data access policies, implementing data security measures, and ensuring that data is easily searchable and retrievable.
- Data Maintenance: Data is regularly maintained to ensure accuracy and completeness. This stage involves implementing data validation and cleansing processes, managing data updates and changes, and ensuring data consistency across systems.
- Data Archiving: Data is archived for long-term retention and compliance. This stage involves defining data retention policies, implementing secure archiving solutions, and ensuring that archived data remains accessible and usable.
- Data Disposal: Data is properly disposed of when no longer needed. This stage involves defining data disposal policies, implementing secure data destruction methods, and ensuring that data is disposed of in compliance with regulatory requirements.
How to Implement an Effective DLM Strategy?
Implementing an effective DLM strategy involves several steps:
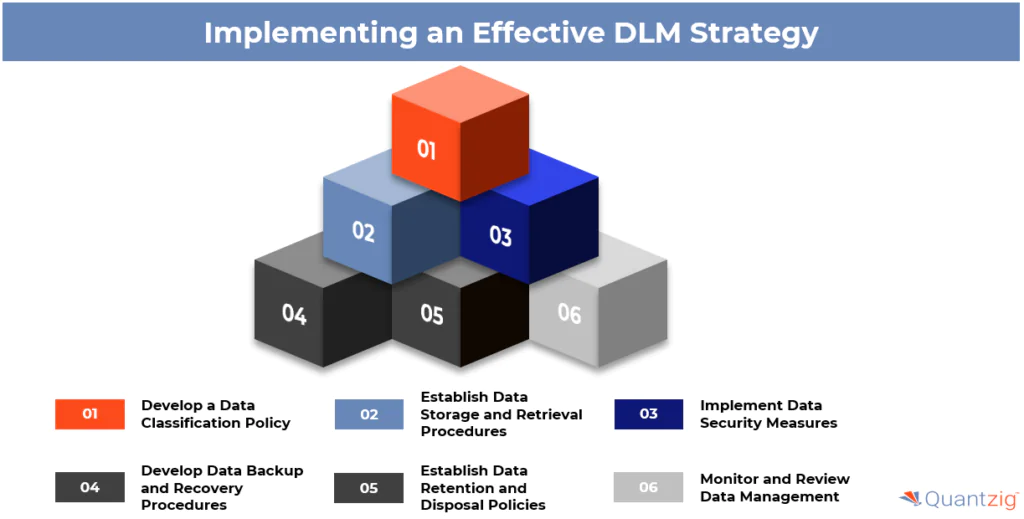
- Develop a Data Classification Policy: Classify data based on its sensitivity and importance. This helps to prioritize data management efforts and ensures that sensitive data is properly secured.
- Establish Data Storage and Retrieval Procedures: Establish procedures for storing and retrieving data. This includes defining data storage formats, implementing data indexing and cataloging systems, and ensuring that data is easily searchable and retrievable.
- Implement Data Security Measures: Implement measures to ensure data security, such as encryption and access controls. This includes defining user access policies, implementing multi-factor authentication, and regularly monitoring and auditing data access.
- Develop Data Backup and Recovery Procedures: Implement robust backup and recovery procedures to ensure that data can be restored in the event of a disaster or data loss. This includes defining backup schedules, implementing secure offsite storage, and regularly testing backup and recovery processes.
- Establish Data Retention and Disposal Policies: Define data retention policies based on regulatory requirements and business needs. Implement secure data disposal methods to ensure that data is properly destroyed when no longer needed.
- Monitor and Review Data Management: Regularly monitor and review data management processes to ensure compliance and effectiveness. This includes conducting regular audits, monitoring data usage and access patterns, and making adjustments to data management policies and procedures as needed.
Benefits of DLM Implementation
Incorporating an advanced data management plan offers numerous advantages for businesses, making Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) a strategic necessity. One of the primary benefits is improved data security, as it ensures data is safeguarded against unauthorized access, thereby minimizing the risk of breaches and cyberattacks. It also promotes better compliance with regulatory standards, reducing the likelihood of legal penalties and reputational harm.
DLM enhances data integrity by keeping information accurate and complete, which supports sound decision-making. Additionally, it improves data availability, ensuring that data is readily accessible when needed to support smooth business operations. Another significant advantage is cost efficiency, as effective data archiving and disposal practices help reduce unnecessary storage expenses. Lastly, DLM contributes to greater business agility, enabling organizations to adapt swiftly to evolving market demands and seize new opportunities, thereby fostering innovation and growth.
Experience the advantages firsthand by testing a customized complimentary pilot designed to address your specific requirements. Pilot studies are non-committal in nature.
Request a free pilot7 Best Tools and Technologies for Data Lifecycle Management
Several tools and technologies are used for data lifecycle management, including:
- Data Management Platforms: Platforms that provide data storage, retrieval, and management capabilities, such as data warehouses, data lakes, and cloud storage solutions.
- Data Encryption Tools: Tools that encrypt data to ensure security, such as file encryption software and database encryption solutions.
- Access Control Systems: Systems that control access to data, such as identity and access management (IAM) solutions and role-based access control (RBAC) systems.
- Data Archiving Tools: Tools that archive data for long-term retention and compliance, such as tape backup systems and cloud archiving solutions.
- Data Disposal Tools: Tools that properly dispose of data when no longer needed, such as secure data erasure software and physical data destruction services.
- Data Governance Tools: Tools that support data governance initiatives, such as data catalogs, data lineage tools, and data quality management solutions.
- Data Backup and Recovery Tools: Tools that support data backup and recovery, such as backup software, disaster recovery solutions, and business continuity planning tools.
Common Challenges and Solutions in DLM
Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) comes with several common challenges that organizations must address to ensure effective data handling. One major issue is data overload, where managing vast amounts of information from diverse sources and in multiple formats becomes increasingly complex. Data security is another significant challenge, especially as cyber threats grow more sophisticated and regulatory requirements continue to evolve.
Maintaining regulatory compliance is also difficult due to the complexity and frequent changes in data protection laws. Additionally, data silos can form when information is isolated within separate systems or departments, hindering seamless data access and integration across the organization. Finally, maintaining data quality is a persistent challenge, particularly when handling large volumes of data from varied sources, which can lead to inconsistencies and inaccuracies if not properly managed.
Solutions to these challenges include:
Effective Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) involves several key practices that enhance data security, accessibility, and usability. Data classification is essential for prioritizing data management efforts by categorizing information based on its sensitivity and importance, ensuring that critical data receives appropriate protection. Data encryption safeguards information by making it unreadable to unauthorized users, while access control ensures that only authorized personnel can view or manipulate sensitive data. Data archiving helps reduce storage costs and supports regulatory compliance by securely storing infrequently used data.
To overcome the limitations of isolated systems, data integration consolidates information from multiple sources, improving accessibility and usability across the organization. Additionally, data quality management ensures that data remains accurate, complete, and consistent throughout its lifecycle, supporting better decision-making and operational efficiency.
DLM vs ILM
Data lifecycle management (DLM) and information lifecycle management (ILM) are often used interchangeably, but there are key differences:
| Aspects | Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) | Information Lifecycle Management (ILM) |
| Data Types | Manages structured and unstructured data within databases and data warehouses. DLM focuses on data in its raw form, regardless of format. | Manages a wide variety of information types, including structured data, documents, multimedia files, emails, and other digital assets. ILM handles diverse content types with different storage and retrieval requirements. |
| Compliance | Ensures adherence to data compliance regulations and standards throughout the data lifecycle. This includes privacy regulations like GDPR and industry-specific standards. | Extends compliance efforts to encompass a broader spectrum of information governance, covering legal, regulatory, and organizational policies. ILM ensures that all information is managed in accordance with relevant laws and guidelines. |
| Lifecycle Phases | Involves distinct phases such as data creation, storage, processing, analysis, distribution, archiving, and eventual disposal. DLM manages data through each phase, optimizing processes for efficiency and data quality. | Encompasses a broader set of lifecycle phases beyond data management, including content creation, classification, access control, versioning, sharing, collaboration, and eventual disposition. ILM orchestrates these phases to ensure seamless information flow across the organization. |
| Integration | Integrates with various data management tools and systems such as databases, data lakes, ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes, and data governance platforms. DLM ensures data consistency and interoperability across these systems. | Requires integration with diverse information systems, including document management systems, enterprise content management platforms, collaboration tools, and knowledge bases. ILM facilitates seamless integration to enable unified access and management of information assets. |
| Scope | Focuses on the entire lifecycle of data, which includes creation, storage, usage, and disposal. DLM primarily deals with raw data and databases. | Focuses on the entire lifecycle of information, which includes data, documents, records, and other digital assets. ILM encompasses a broader range of digital content. |
| Scope of Management | Typically involves managing data within a single organization. DLM processes are often confined to internal systems and databases, ensuring data integrity and compliance within the organization. | Involves managing information across multiple organizations and systems. ILM includes collaboration and information exchange between different entities, ensuring comprehensive information governance. |
Effective data lifecycle management involves meticulous data collection, thorough data processing, secure data sharing, and ensuring data usability while maintaining strict compliance and governance standards. These practices are crucial across any industry sector to optimize data integrity, enhance operational efficiency, and support informed decision-making.
DLM for Business Success
Effective DLM is critical for business success, as it ensures that data is properly managed throughout its lifecycle. This supports business operations, decision-making, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
By implementing effective DLM practices, organizations can:
1. Improve Data-Driven Decision Making: Effective data management ensures that data is accessible, accurate, and usable, enabling better decision-making.
2. Enhance Customer Experience: Effective data management helps organizations to better understand customer needs and preferences, enabling them to deliver better products and services.
3. Reduce Costs: Effective DLM can reduce storage costs, improve operational efficiency, and reduce the risk of fines and penalties associated with non-compliance.
4. Mitigate Risks: Effective DLM helps to mitigate risks associated with data breaches, cyber attacks, and regulatory non-compliance.
5. Drive Innovation: Effective data management enables organizations to leverage data to drive innovation and gain a competitive advantage.
Phases of Data Lifecycle Management
In any industry sector, robust data lifecycle management is essential, starting with accurate data collection and efficient data processing to transform raw data into valuable insights. Ensuring secure data sharing and maintaining data usability are critical for leveraging data effectively, all while adhering to stringent compliance and governance requirements to protect data integrity and meet regulatory standards.
The phases of data lifecycle management include:
1. Data Creation: Data is created and stored in a secure and organized manner. This phase involves defining data requirements, establishing data sources, and implementing data capture processes.
2. Data Storage: Data is stored in a secure and accessible manner. This phase involves selecting appropriate storage solutions, implementing backup and recovery procedures, and ensuring data redundancy.
3. Data Retrieval: Data is retrieved and used for business operations and decision-making. This phase involves developing data access policies, implementing data security measures, and ensuring that data is easily searchable and retrievable.
4. Data Maintenance: Data is regularly maintained to ensure accuracy and completeness. This phase involves implementing data validation and cleansing processes, managing data updates and changes, and ensuring data consistency across systems.
5. Data Archiving: Data is archived for long-term retention and compliance. This phase involves defining data retention policies, implementing secure archiving solutions, and ensuring that archived data remains accessible and usable.
6. Data Disposal: Data is properly disposed of when no longer needed. This phase involves defining data disposal policies, implementing secure data destruction methods, and ensuring that data is disposed of in compliance with regulatory requirements.
6 Benefits of Data Lifecycle Management
The benefits of data lifecycle management include:
- Improved Data Security: Data is properly secured to prevent unauthorized access, reducing the risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks.
- Improved Data Compliance: Compliance with regulatory requirements is ensured, reducing the risk of fines and reputational damage.
- Improved Data Integrity: Data integrity is maintained, ensuring that data remains accurate and complete, and supporting better decision-making.
- Improved Data Availability: Data is accessible and usable when needed, supporting business operations and decision-making.
- Cost Savings: Effective DLM can reduce storage costs by ensuring that data is properly archived and disposed of, optimizing storage resources.
- Improved Business Agility: Effective data management enables organizations to respond quickly to changing business needs and opportunities, supporting innovation and growth.
Quantzig: Experts in Data Lifecycle Management
Quantzig is a leading data analytics and advisory firm that specializes in helping organizations implement effective data lifecycle management strategies. With years of experience in data management and analytics, Quantzig’s team of experts has a deep understanding of the challenges and best practices associated with DLM. Quantzig’s services include:
- Data Governance: Quantzig helps organizations develop and implement effective data governance policies and procedures to ensure data quality, security, and compliance.
- Data Architecture: Quantzig designs and implements data architectures that support effective data management, including data storage, retrieval, and integration.
- Data Security: Quantzig helps organizations implement robust data security measures to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyber attacks.
- Data Archiving and Disposal: Quantzig helps organizations develop and implement effective data archiving and disposal policies to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and optimize storage resources.
- Data Quality Management: Quantzig helps organizations implement data quality management processes to ensure that data remains accurate, complete, and consistent throughout its lifecycle.
- Data Analytics: Quantzig helps organizations leverage data analytics to gain insights and drive business success, supporting data-driven decision-making and innovation.
By partnering with Quantzig, organizations can ensure that their data is properly managed throughout its lifecycle, supporting business success and driving innovation.
Get started with your complimentary trial today and delve into our platform without any obligations. Explore our wide range of customized, consumption driven analytical solutions services built across the analytical maturity levels.
Start your free trialConclusion
Data lifecycle management is a key component of contemporary data management, ensuring that data is properly managed throughout its entire lifecycle. Effective DLM involves several key stages, from data creation to disposal, and ensures that data remains accessible, secure, and compliant with regulatory requirements.
By implementing an effective DLM strategy, organizations can improve data security, compliance, integrity, availability, and cost savings, ultimately supporting business success. With the help of tools and technologies such as data management platforms, encryption tools, and access control systems, organizations can effectively manage data throughout its lifecycle.
However, implementing an effective DLM strategy is not without its challenges. Organizations must address issues such as data overload, data security, and data compliance, and develop solutions such as data classification, encryption, and access control to overcome these challenges.
Ultimately, DLM plays an essential for business success in today’s data-driven world. By properly managing data throughout its lifecycle, organizations can leverage data to drive innovation, improve decision-making, and gain a competitive advantage.