Written By: Sudeshna Ghosh
Table of Contents
Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of modern manufacturing, the emergence of Smart Factory 4.0 represents nothing short of a revolution. By leveraging cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, IoT, and advanced robotics, Smart Factories have become the vanguard of industrial progress. Gone are the days of traditional assembly lines and manual labor; in their place stands a dynamic, interconnected ecosystem of digitized production facilities, networked devices, and human expertise. This article explores the profound impact of Smart Factories on the manufacturing industry, unveiling the transformative potential they hold in optimizing efficiency, quality, and competitiveness through Big Data analytics and evidence-based decision-making. Brace yourself for a journey into the future of manufacturing, where innovation meets automation, powered by cloud computing and supported by smart manufacturing tools, to redefine the very essence of production while ensuring data protection and cyber security. Moreover, smart warehouses, smart farming, cyber security, software solutions, product development, networked plants, machine learning, the 4 levels of a Smart factory, smart connected factories, big data analysis, and digital twins all play pivotal roles in shaping the landscape of Smart Manufacturing.
Book a demo to experience the meaningful insights we derive from data through our smart factory platform capabilities. Schedule a demo today!
Request a Free DemoBenefits of Smart Factory and Its Impact on Manufacturing:
The significance of Smart Factory 4.0 in manufacturing is profound, as it spearheads a paradigm shift through automation, resource optimization, and waste reduction. By integrating artificial intelligence, Big Data analytics, and machine learning, Smart Factories transform traditional production methods into smart manufacturing processes. This transition is facilitated by networked devices and digitized production facilities, supported by cloud computing and software solutions that enable real-time monitoring and control. Moreover, the implementation of smart manufacturing tools enhances operational efficiency and quality assurance across networked plants. The evolution through the 4 levels of a Smart factory emphasizes evidence-based decision-making, ensuring continuous improvement and innovation in product development. Concurrently, Smart Factories prioritize data protection and cybersecurity to safeguard sensitive information, reflecting a commitment to maintaining the integrity of big data analysis and digital twins. This holistic approach not only revolutionizes production processes but also paves the way for advancements in smart warehouses and smart farming, reshaping the future of manufacturing.
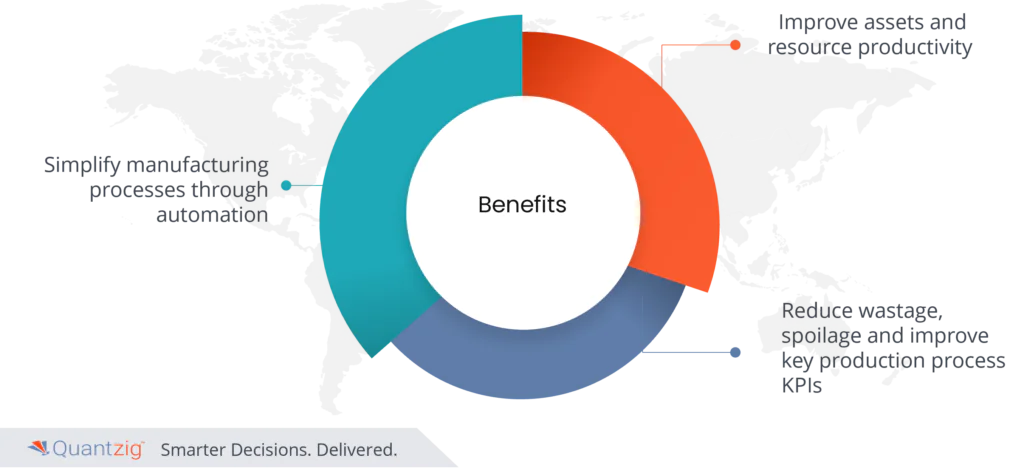
1. Simplify manufacturing processes through automation
Smart Factories revolutionize manufacturing processes through automation, leveraging robotics, AI-driven machinery, and IoT sensors to streamline operations previously reliant on human labor. This transformative approach not only enhances efficiency but also minimizes errors, ensuring consistent and high-quality outputs. By embracing automation, manufacturers can reduce labor costs, enhance production speed, and achieve precision, thereby strengthening their competitiveness in today’s dynamic market landscape. This transition towards automation aligns with the evolution of networked plants and smart connected factories, underpinned by big data analysis and machine learning algorithms. Moreover, it emphasizes the importance of evidence-based decision-making supported by insights derived from digital twins, while prioritizing data protection and cybersecurity to safeguard sensitive information throughout the 4 levels of a Smart connected factory.
2. Improve assets and resource productivity
Smart Factories harness the power of big data analysis and machine learning to drive optimization through real-time monitoring and data analytics. By utilizing evidence-based decision-making, manufacturers can proactively maintain machinery and equipment in networked plants, preventing breakdowns and ensuring maximum uptime. This approach extends to resource management, where raw materials are efficiently managed to avoid overstocking or underutilization. The integration of digital twins in smart connected factories facilitates a deeper understanding of production processes, enabling manufacturers to operate at the highest of the 4 levels of a Smart connected factory. Moreover, robust data protection and cybersecurity measures ensure the integrity of sensitive information. The significance of these practices lies in achieving cost savings and promoting sustainable practices, as manufacturers optimize their operations with fewer resources, thereby reducing their environmental footprint and operational expenses while advancing in product development.
3. Reduce wastage, spoilage and improve key production process KPIs
The data-driven approach of the Smart Factory 4.0 enables precise control over production processes, facilitated by artificial intelligence and Big Data analytics. This results in a reduction of wastage and spoilage, as deviations from quality standards are promptly identified and corrected in real time. Through continuous monitoring of key production process KPIs using networked devices and smart manufacturing tools, such as yield, cycle times, and defect rates, improvements are made to enhance both product quality and operational efficiency. The utilization of cloud computing and software solutions further enhances this process, ensuring seamless integration of digitized production facilities. Ultimately, this approach leads to improved profitability, resource conservation, and heightened customer satisfaction, while also laying the foundation for advancements in smart warehouses and smart farming.
In summary, the Smart Factory’s impact on manufacturing is transformative. It empowers manufacturers to automate processes, make the most of their resources, and drive efficiency gains that result in cost savings, environmental benefits, and increased competitiveness. By embracing Smart Factory Benefits and principles, manufacturers can adapt to the ever-changing demands of the market and pave the way for a more sustainable and efficient future in manufacturing. This entails leveraging digital technology and augmented reality solutions such as TeamViewer’s frontline software to enhance operational efficiency and facilitate growth. Implementing a strategic roadmap for technological improvements, particularly in sectors like food and beverage manufacturing, enables manufacturers to optimize their machinery and enhance their brand while ensuring privacy and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Experience the advantages firsthand by testing a customized complimentary pilot designed to address your specific smart factory requirements. Pilot studies are non-committal in nature.
Request a Free PilotChallenges faced while implementing Smart Factory:
Implementing Smart Factory initiatives presents a myriad of challenges that necessitate careful consideration and strategic planning after scanning the information. From optimizing the supply chain to empowering personnel with new skills and technologies, navigating these obstacles requires a holistic approach that emphasizes collaboration, knowledge sharing, and effective communication. As companies strive to enhance productivity and drive engagement among their workforce, ensuring the competence of personnel becomes paramount to achieving manufacturing goals. Harnessing the power of data insights is essential for informed decision-making, enabling companies to maximize resource usage while optimizing operational plant performance. Realizing the full potential of Smart connected factory initiatives also entails embracing real-time reporting mechanisms and fostering a culture of continuous problem-solving to minimize downtime and maximize uptime. In this landscape of technological advancement and innovation, addressing these challenges is essential for companies seeking to thrive in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
1. Highly Manual Processes:
Transitioning from traditional manufacturing to a Smart Factory often entails grappling with the challenge of modernizing highly manual processes. Many existing setups heavily rely on manual labor and outdated methodologies, hindering the seamless integration of automation and digitalization. Resistance from the workforce can emerge as a significant obstacle, necessitating retraining efforts and raising concerns about potential job displacement. Addressing this challenge demands the implementation of effective change management strategies, transparent communication, and a commitment to enhancing workforce skills for the operation and maintenance of new automated systems. This transition involves leveraging machines, sensors, and the Industrial Internet of Things (IoT) to optimize production systems and minimize downtime and waste. By harnessing data analytics and augmented reality (AR), Smart Factories can enhance quality control and streamline logistics while maximizing underutilized production capacity and conserving resources. Through improved connectivity and diagnostics, Smart Factory operations can transition from reactive to proactive, utilizing action-oriented data to drive efficiency and productivity. Additionally, the adoption of technologies such as smart glasses empowers workers with real-time information and support, facilitating smoother operations and ensuring a successful transition to the era of Industry 4.0. In this journey, considerations for production costs and planning in the context of Traditional manufacturing are paramount. Effective management of active data plays a crucial role in optimizing processes and decision-making, paving the way for sustainable growth and competitiveness in the evolving manufacturing landscape.
2. Lack of IT Infrastructure in Plants to Set Up Digital Ecosystems:
Integrating a digital ecosystem within manufacturing plants often encounters obstacles due to deficient IT infrastructure. Older facilities might lack the requisite networking capabilities, robust cybersecurity measures, or efficient data management systems necessary for deploying Smart Factory technologies. Overcoming this hurdle necessitates investments in modernizing plant infrastructure, encompassing network connectivity, data storage, and cybersecurity protocols, to facilitate the smooth integration of digital technologies. This ensures the integrity and security of data, enhancing plant efficiency and supporting functions such as automation, production tracking, and decision-making throughout the value chain. Upgrading infrastructure also enables tactical intervention, issue resolution, and the implementation of automatic reporting structures for continual production improvement. Moreover, it empowers predictive maintenance capabilities, reducing downtime and enhancing asset utilization. By addressing these deficiencies, manufacturers can enhance on-time delivery, mitigate human errors, bolster food safety, and maintain quality standards while optimizing machine instructions and delivery methods. Additionally, this transformation facilitates the reduction of manual handling, streamlines tracking products from raw materials to packaging and delivery, ensures safety standards, enables efficient data exchange within an integrated system, and leverages data analytics for informed decision-making. Furthermore, it enables training staff effectively, implementing feedback loops for continual improvement, and predicting failures through Total Productive Maintenance strategies to ensure on-time delivery and processing efficiency.
3. Legacy Processes Involving Complex Workflows:
A significant challenge lies in overcoming legacy processes characterized by intricate workflows entrenched within the organization over many years. Transitioning to streamlined, data-driven workflows necessitate meticulous process reengineering efforts. Thorough analysis of existing workflows is crucial to identify inefficiencies and plan the transition meticulously, minimizing disruptions in production. This challenge highlights the importance of meticulous planning and a phased approach to adopting smart factory benefits, ensuring minimal disruptions and maximal benefits.
This hurdle also intersects with various critical aspects of operations and management. It requires considerations such as optimizing human resources allocation, predicting and mitigating failures, and reducing human errors through inline quality checks and real-time monitoring. Additionally, it involves enhancing energy efficiency by optimizing the factory’s lights and overall energy consumption. Integrating information and operations across IT/OT infrastructure and addressing concerns regarding corporate security and silos of information are imperative. Establishing a unified production environment while ensuring information security and protecting intellectual property are paramount. Moreover, it necessitates harnessing human ingenuity, creativity, and knowledge to foster sustainable growth.
Central to this challenge is ensuring data availability and conducting proactive data analysis to drive informed decisions. By addressing these multifaceted considerations, organizations can effectively navigate the transition to streamlined workflows and realize the full potential of smart factory benefits.
Quantzig’s Success Story
Client Details:
A leading spirit manufacturing company operating in the UK and Europe
The challenges faced by the Client:
Firstly, highly manual processes pervaded their manufacturing operations, leading to inefficiencies, increased operational costs, and a susceptibility to errors. These labor-intensive processes were resistant to change, necessitating comprehensive workforce retraining and change management strategies to successfully transition to automated methods.
Secondly, their manufacturing plants lacked the requisite IT infrastructure to establish robust digital ecosystems. This posed significant hurdles in terms of connectivity, data management, and cyber security. To address this, our client needed to make substantial investments in upgrading their plant infrastructure, ensuring it could support the seamless integration of digital technologies while safeguarding data integrity.
Lastly, the presence of legacy processes characterized by complex workflows added another layer of complexity. These entrenched workflows hindered agility and productivity. Reengineering these processes necessitated meticulous planning and a phased approach to minimize disruptions during the transition.
In essence, our client faced the formidable task of modernizing their manufacturing operations by addressing these challenges, ultimately embracing the transformative power of the Smart Factory to enhance efficiency, competitiveness, and sustainability in an evolving industrial landscape.
Solutions offered by Quantzig:
Quantzig played a pivotal role in helping our client streamline their manufacturing operations by providing an integrated production planning tool that seamlessly combined demand planning, capacity planning, and MRP (Material Requirements Planning) planning. This innovative solution allowed our client to harmonize their production processes, ensuring that they could efficiently meet customer demand while optimizing resource allocation and minimizing inventory costs.
Furthermore, our expertise extended to the development of simulators for capex (capital expenditure) planning based on capacity and demand forecasts. These simulators provided our client with invaluable insights into the most strategic investments for capacity expansion, aligning capital allocation with anticipated future needs.
In addition, we implemented digital twins for their factories, enabling real-time optimization of manufacturing processes. By leveraging digital replicas of their production facilities, our client could fine-tune operations for high equipment utilization, reduced operational costs, and alignment with the demand plan. This dynamic approach to process optimization ensured that our client could meet market demands efficiently while maintaining profitability.
In essence, Quantzig’s comprehensive solutions empowered our client to achieve operational excellence, enhance cost-efficiency, and align their production capabilities with market demands, ultimately driving sustainable growth and competitiveness in their industry.
Get started with your complimentary trial today and delve into our platform without any obligations. Explore our wide range of customized, consumption driven analytical solutions services built across the analytical maturity levels.
Start your Free TrialImpact Delivered:
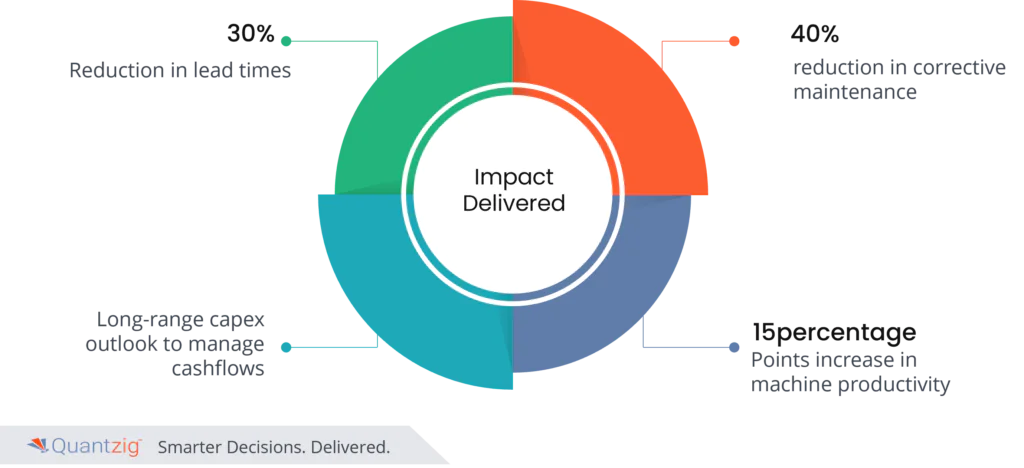
Achieving a 30% reduction in lead times, enhancing long-range capex outlooks to manage cash flows effectively, realizing a 15 percentage points increase in machine productivity, and attaining a 40% reduction in corrective maintenance represent pivotal milestones in our journey towards sustainable growth. These accomplishments are underpinned by our ability to predict failures accurately, optimize information and operations synergistically, leverage creativity to innovate solutions, and harness knowledge to drive continuous improvement. By integrating these strategies, we position ourselves for sustainable growth while optimizing operational efficiency and enhancing productivity across the board.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Smart Factory stands as a beacon of innovation and transformation in the realm of manufacturing. Its impact is nothing short of revolutionary, as it reshapes traditional paradigms of production. By automating processes, optimizing resources, and reducing wastage, the Smart Factory ushers in a new era of efficiency and sustainability. It empowers manufacturers to thrive in an increasingly competitive global market, delivering higher-quality products while minimizing costs. As this digital evolution continues to unfold, the smart factory benefits cannot be overstated. It represents the future of manufacturing, a future where technology and human expertise harmoniously coexist, driving progress, prosperity, and a more sustainable world. Embracing the Smart Factory is not merely a choice; it is an imperative for manufacturers to adapt, evolve, and lead in an era where innovation is the key to success.